Table of Contents
- The Big Why – Cost of a Data Breach
- Cost of Downtime
- How to Calculate Downtime Costs
- What do an Ogre, an onion, and network security have in common?
- Summary of Security Solutions for Small Businesses
- How to Get Started
- Here to Help
The news is full of the latest companies that have suffered security breaches. These headlines focus on large corporations because the big numbers involved make the attack more impressive. This gives many small business owners a false sense of security -an illusion that there is security through obscurity. There is an idea that a “small business like mine” won’t get attacked.
This is a false assumption. Hackers generally use automated scanning tools to comb the internet for a specific vulnerability. They’re not looking for a big name. An open door or window will do. Once they get in, they will determine what data is valuable and extort it. Big name or not.
Is IT security for small businesses necessary? Absolutely.
The challenge is that there are a million products and solutions out there that promise to protect your data.. Most business owners aren’t IT professionals. They don’t have time or inclination to sort through every security solution and understand the benefits and costs.
How can you tell what matters most when it comes to IT security for small businesses? This guide is made to point you in the right direction and get you thinking about IT security. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, and the best security solutions are usually tailored to how you do business. i.t.NOW can help with this, but we hope this guide gives you helpful info that will help you start protecting your business.
The Big Why – Cost of a Data Breach
“According to the Ponemon Institute’s 2020 “Cost of Data Breach Study,” the global average for a data breach is $3.83 million, but the average cost of a data breach in the United States has hit an all-time high of $8.64 million.” – Secureworks
Those may seem like huge numbers, and they are. However, it’s likely that they are severely under reported. Privately held companies that don’t have to meet government compliance or undergo cyber security audits frequently choose to not report when they’ve been breached. Here are some other startling statistics surrounding data breaches.
- The total number of malware infections have been on the rise for the last ten years.
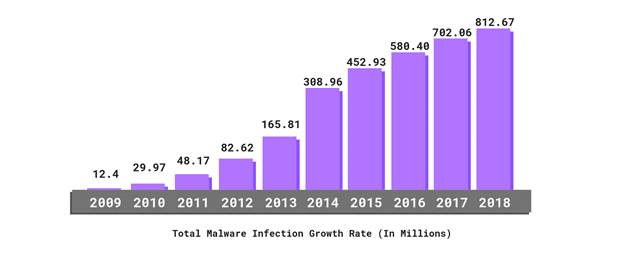
- 34% of businesses hit with malware took a week or more to regain access to their data.
- 58% of malware attack victims are categorized as small businesses.
- Ransomware attacks are growing more than 350% annually.
- CEO fraud is now a $12 billion scam.
- Only 3% of targeted users report malicious emails to management.
- 43% of data breaches involved small businesses.
- 29.6% of companies will experience a data breach in the next two years.
- 47% of small businesses had at least one cyber-attack in the past year, and 44% of those had two to four attacks.
- 70% of small businesses are unprepared to deal with a cyber-attack.
- In 2018, cyber-attacks cost small businesses an average of $34,604.
Unfortunately, network security threats are evolving constantly, and the cost of a data breach keeps increasing. Small business owners need to better understand and invest in proper protection for their businesses. This is not a problem that is going away and is one that could devastate your business if the worst happened.
Cost of Downtime
If that wasn’t enough reason to get your security house in order, lets examine the cost of downtime. The reason that downtime is so expensive is that you’ve not only lost revenue, but you also suffer lost productivity, have recovery costs, and experience reputation loss as well.
Encomputers shares a great example of how downtime is calculated.
How to Calculate Downtime Costs
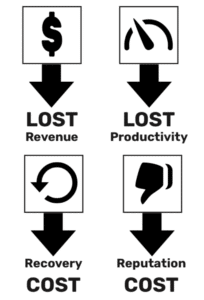
At a high level, downtime costs have four components: lost revenue, lost productivity, recovery costs, and reputation costs. Let’s consider a fictional company with $10 million in annual revenue and 50 employees that experiences unplanned downtime lasting just one day. What will their downtime costs look like?
First, let’s calculate lost revenue. A company with $10 million in annual revenue has an average weekly revenue of $192,308, or $4808 per hour.
$10M annual revenue / 52 weeks = $192308 average weekly revenue
$192308 / 40 hours per week = $4808 average hourly revenue
Next, we’ll determine lost productivity. In December 2020, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that private industry average employee compensation including wages and benefits was $36.23 per hour. Assuming our fictitious company’s employee productivity is reduced by 75% during this episode, one hour of downtime will cost the company $1358.63 in lost productivity.
50 employees * $36.23/hour total compensation * .75 lost productivity = $1358.63 lost productivity per hour
Putting these two figures together, we can see that during the one-day outage, our fictional company lost $49,336 in revenue and productivity. Depending on the cause of the outage, they may have incurred recovery costs such as new hardware, overtime for their sole IT generalist, or consulting fees. In addition, the nature of the outage may have impacted their reputation with clients.
($4808 + 1359) * 8 hours = $49336 lost productivity and revenue in one day
As we described previously, “these expenses could be hidden in different categories – labor, marketing, operating expenses, and capital expenses could all be increased due to outdated or inefficient technology. These costs can even be lurking in accounts receivable, in the form of longer payment cycles and more overdue invoices and write-offs.” It is important to weigh your unique business considerations in order to arrive at your true cost of downtime.
As you can see the cost of downtime can be significant even for a small business. The larger your organization grows the higher your cost of downtime will be. Regardless of your business’s size, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
Now that we’ve identified the clear and present danger that lax IT security for small businesses presents, lets talk about how to keep your organization safe.
What do an Ogre, an onion, and network security have in common?
The answer is that they all have layers. 7 layers to be exact. Mindsight had a great summary on their website. We’ll dive into 5 of these layers that are most important to small businesses and discuss the solutions that would typically be associated with each.
The 7 Layers Of Cybersecurity
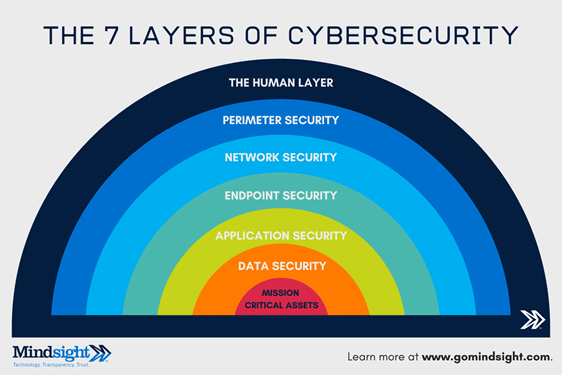
The 7 layers of cybersecurity should center on the mission critical assets you are seeking to protect.
1: Mission Critical Assets – This is the data you need to protect*
2: Data Security – Data security controls protect the storage and transfer of data.
3: Application Security – Applications security controls protect access to an application, an application’s access to your mission critical assets, and the internal security of the application.
4: Endpoint Security – Endpoint security controls protect the connection between devices and the network.
5: Network Security – Network security controls protect an organization’s network and prevent unauthorized access of the network.
6: Perimeter Security – Perimeter security controls include both the physical and digital security methodologies that protect the business overall.
7: The Human Layer – Humans are the weakest link in any cybersecurity posture. Human security controls include phishing simulations and access management controls that protect mission critical assets from a wide variety of human threats, including cyber criminals, malicious insiders, and negligent users.
As you can see there is some complexity to cyber security. Cybercriminals are constantly changing their methods of attack, and a layered security approach helps us be best prepared to defend. Let’s start like we would with an onion. From the outside in.
The Human Layer
People are hard to deal with if you’re a cyber security professional. They’re imperfect. Illogical. They will believe in and click on just about anything. You know why that Nigerian prince scam went on for YEARS AND YEARS? People kept falling for it.
So, the question becomes “How do we make our people smarter?”
Train them.
- 98% of cyber attacks rely on social engineering. – Purplesec
Cyber security training is essential for every business. You need to make sure your employees understand how to recognize threats and avoid common traps. Proper training can help them detect and avoid phishing, malware, and password breaches.
So how do you teach your employees to stay safe online? There are a variety of training resources available. Most small businesses won’t have internal resources that can lead a training of this kind, but luckily there are security companies that you can book an in-person training session with.
If your business has remote workers that makes an in-person training hard there are a couple of companies such as mimecast and knowbe4 that have created online training modules that help end users.
Human Solutions
In addition to training your employees it helps to have an acceptable use policy that all employees sign when they begin employment. This allows you to enforce policy on users that are continually getting into trouble surfing sketchy sites or clicking on things they shouldn’t.
The last thing you can do to secure the humans that use your network is design your security with them in mind. That means it must be simple and intuitive. Security measures that are too complex or difficult to use force users to get “creative”. If users are so irritated by your security that they’re finding “work arounds” to subvert the system, you’ve likely created a larger problem.
Passwords are a good example. Users hate passwords. They don’t like remembering them, and they especially don’t like changing them. This causes them to have terrible password hygiene. They reuse passwords all over even though they are not supposed to. Passwords are not complex enough unless you force complexity on them. When they do change a password, they change just a couple of characters. Design simple security so that users can adopt and adapt.
The Perimeter Security Layer
Network perimeter security is a boundary between your internal network and the internet. It’s the edge of what your company has control over.
Most small businesses use a firewall to manage what traffic they allow to enter their internal network. There are several additional layers of security that can be added at the perimeter such as Intrusion Prevention System, Advanced Threat Protection, Gateway Antivirus, and Content Filtering.
Firewall – A firewall is a security device designed to prevent unauthorized access into or out of a computer network. It serves as a gatekeeper that allows or blocks access to the network based on a defined set of rules that an IT admin programs it with. This is one of the most basic and needed pieces of network security equipment that a small business can own.
Many next generation firewalls have a software security suite that adds additional protection to the network. These are effective tools at keeping you safe and are highly recommended. Many of the other items concerning perimeter security are simply a software license you purchase and configure on your firewall.
Advanced Threat Protection – ATP is a software suite that allows you to protect against know and unknown threats. It does this by leveraging a sandbox technology. If an unknown threat enters the network, ATP will trap it in the sandbox and then check it against multiple cloud repositories for known threats. Anything determined malicious it is blocked. If the check comes back clean it is sent through. Unknown processes or software are blocked until a verdict is reached to protect against zero-day threats.
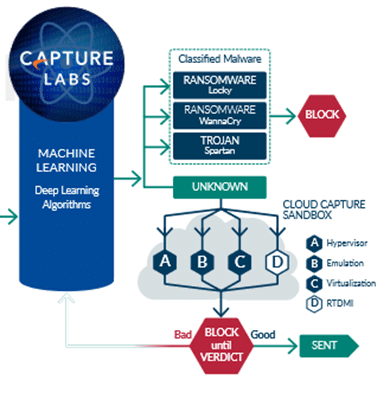
Intrusion Prevention System – An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a network security tool that continuously monitors a network for malicious activity and takes action to prevent it, including reporting, blocking, or dropping it, when it does occur.
This means that if you have IPS enabled on the firewall and someone tries a brute force attack (they have a software that tries to log in with every known password) it can not only detect the intrusion, but it also blocks the attack. This is a great line of defense.
Gateway Antivirus – Gateway Antivirus uses deep packet inspection on all traffic that hits the firewall. If any of that traffic has virus signatures that match the cloud virus databases the attacks are suppressed before they get to desktops on the network.
Gateway AV can also protect you against malicious downloads. When a user makes a request to download a file from the web, that file is analyzed. If a virus is found the file is then discarded.
Content Filtering – This service on the firewall lets you enforce internet use policies and control access to inappropriate, unproductive, and potentially illegal web content. You can block access to specific website or block an entire category such as pornography or hate speech. You can also block time wasting sites such as social media or ESPN. This allows you to control what websites can be visited form inside the company network.
A firewall is a critical piece to a good plan for perimeter security. A quality next generation firewall properly configured with a suite of tools like the ones mentioned above will give quality protection to you and your team. Solutions can be configured by your IT admin easily with the right firewall hardware and software licensing.
The Network Security Layer
There seems to be some debate among IT professionals as to exactly what solutions fall within the network security layer. For our purposes we’ll discuss the solutions that happen on networking equipment, including switches, servers and wireless. Naturally, there will be some overlap between layers as some of the solutions work for both endpoint and network security.
Access Control – Users on the network should have access to only the resources that they need access to an no more. This is sometimes called zero trust network access. In practical terms this means that we have a system in place that allows us to grant users specific permissions about the data and applications they can access.
In most cases this is done via group policy on a server called a domain controller. A DC allows us to control what files a user can see and what they have permissions to. The function of their role within the organization typically determines those needs and working with management we create permissions according to established policy.
More companies have moved to the cloud, and many won’t have a local DC anymore. These organizations can still benefit from access control by leveraging Azure AD. This gives similar functionality to a local DC in a cloud environment.
If Azure AD isn’t a fit for your company based on the applications or data in use, we can still control access via permissions in specific applications and offer management in may cases through remote monitoring and management software.
In addition to permissions and access management a DC or similar solution will allow you to enforce security policies such as password hygiene and manage them across the network. Many other policies can be enforced by something called group policy.
Network Segmentation – Smart network design can help secure critical data and resources. By segmenting the network into smaller pieces, you can limit the attack surface and make it more difficult for an attacker to penetrate network wide.
In addition, smart network segmentation allows you to put data backups on a separate network internally from live production data. That way if an attacker did manage to infect your productions servers there is a chance they would NOT get into your backups as well. Its not a foolproof guarantee, but it adds another step that an attacker might miss.
Network Monitoring and Alerting – Networks should be monitored and alerted on 24/7. This essentially means that you have a software solution running on servers, switches, etc. that will tell you when things are offline, or when other things are wrong.
A monitor will check that a machine is running within certain specified parameters. If something starts happening that could indicate a problem or an attack it sends off an alert. These alerts allow your IT team to see small things before the become big problems. The ability to be proactive makes a huge difference.
Firmware Updates – All network equipment including firewalls, switches, servers, and more have occasional firmware updates that need to be applied. In many cases these updates address a specific security vulnerability that has been discovered. The best IT providers will have a process for ensuring that firmware updates on network equipment get applied in a timely manner.
Endpoint Security Solutions
Security solutions for endpoint protection are the part of security that has changed the most over the last couple of years. Needs have evolved as the effects of COVID-19 shifted a large portion of the workforce and their endpoints to work from home. This has increased the risk from remote access solutions and cloud applications. Endpoint solutions include secure remote access, multi-factor authentication, patches and updates, endpoint detection and response, and encryption solutions.
Secure Remote Access – As the workforce has moved from the office to home users have needed more flexibility than ever in the way they connect to critical company applications and data. Many apps have been moved to the cloud where users can access them in a browser. Server based resources have necessitated resources such as a secure remote gateway or VPN.
A secure gateway allows a user to connect securely to the office network via a simple log in in a web browser. The user simply visits the designated page and enters their credentials. The gateway then establishes a secure network connection and allows them the needed access.
Alternatively, a VPN has a client that is loaded on the endpoint. They simply open the client, enter credentials and the VPN establishes a secure connect to network resources.
The danger lies when network access is given without a secure solution in place. Out of laziness or lack of knowledge, some IT admins simply open holes in the firewall that endpoints could enter to facilitate remote access. It’s dangerous and opens the organization up to attack. All remote access solutions should be examined for security as they are a popular attack point with bad actors.
Multifactor Authentication – As users have moved to work from home a better way to secure these remote access solutions and web-based applications has become paramount. Enter MFA.
MFA allows you to use an app on your phone, your email, or other method to provide a second layer of authentication. Many of the phone apps allow you to tie it to your biometrics as well. That way you can use your fingerprint on your device to authenticate into a web app or your secure remote access solution.
We recommend enabling MFA on everything possible. “MFA stops 99% of password-based cybercrime in its tracks” according to Microsoft. It’s a big deal, and a simple low cost change you can make to add significant protection to your network.
Patches and Updates – Microsoft releases patches and updates every single week. They are critical to network security and to the protection of your endpoints. The problem is that they frequently take a LONG TIME to apply, and it must be done on every endpoint and every server on the network.
This means that you need a solution that allows you to automate the testing and deployment of patches. Most quality remote monitoring and management software allows you to do just that. You can automate the testing and deployment of patches and even set it to run at night, so it doesn’t bug you during the middle of the workday. This keeps you productive and protected.
Antivirus – Every endpoint needs a quality antivirus solution to keep it safe. The problem with many AV solutions is that they don’t do a good job protecting against ransomware. That’s where endpoint detection and response comes in.
EDR solutions are the next evolution of antivirus and use AI to power their threat detection process. This typically gives them much better results than traditional AV. Most traditional AV simply checked your process or file against a list of know threats and virus definitions. It did very little to protect against zero-day threats (unknown). EDR solutions are much better at this and offer superior protection against ransomware. We recommend a quality EDR solution for all your endpoints.
Encryption – The mobile nature of endpoints has also made device encryption more important than ever. The ability to encrypt your hard drive allows you a level of protection especially against theft. Microsoft offers built in drive encryption with BitLocker that comes recommended.
Application Security
If your company has web applications, or run an ecommerce business with internet facing assets, web application security might be important to you. Imperva gives us a good definition.
Web application security is the process of protecting websites and online services against different security threats that exploit vulnerabilities in an application’s code. Common targets for web application attacks are content management systems (e.g., WordPress), database administration tools (e.g., phpMyAdmin) and SaaS applications.
There are several possible attacks on web resources that range from SQL Injection to DDoS attacks and more. Web application security can help to protect your organization. Here are a couple of solutions that might help if your organization has these needs.
Web Application Firewall – A WAF or web application firewall helps protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet. It typically protects web applications from attacks such as cross-site forgery, cross-site-scripting (XSS), file inclusion, and SQL injection, among others.
By deploying a WAF in front of a web application, a shield is placed between the web application and the Internet. While a proxy server protects a client machine’s identity by using an intermediary, a WAF is a type of reverse-proxy, protecting the server from exposure by having clients pass through the WAF before reaching the server.
DDoS Protection – DDoS stands for distributed denial of service. This is a method of attack where cybercriminals flood a network with so much malicious traffic that it cannot operate or communicate as it normally would. The volume is so high that it causes the networks normal legitimate traffic to also come to a halt.
To stop this kind of attack in years past it would have been necessary for an organization to “overbuild” their network so that it had large enough capacity that it could not be easily taken down by such an attack. Today, most organizations with needs to protect against such an attack will subscribe to a cloud-based DDoS mitigation service that has the resources to defend.
Summary of Security Solutions for Small Businesses
There is a LOT to think about when it comes to network security for a small business. How do we sum it all up? Here is a condensed list of the different parts of security and the solutions you probably need for your business.
The Human Layer
- Cyber Security Training
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Simple Usable Security
Perimeter Protection
- Next Generation Firewall
- Advanced Threat Protection
- Intrusion Prevention Detection
- Gateway Antivirus
- Content Filtering
Network Security Layer
- Access Control
- Network Segmentation
- Network Monitoring and Alerting
- Firmware Updates
Endpoint Security
- Secure Remote Access
- Multifactor Authentication
- Patches and Updates
- Antivirus
- Encryption
Application Security (Not All Small Business Will Need This)
- Web Application Firewall
- DDoS Protection
How to Get Started
Now we’ve discussed the big reasons why network security is so important. We’ve reviewed how a layered security solution will typically offer the best defense for your network, and we’ve dug into many of the specific solutions you’ll probably need for your business.
How do you get started? When eating an elephant, I recommend starting one bite at a time. Start with whatever seems easiest to you and try to put one new thing in place. Then keep moving down the list a little at a time knowing that every item you check off gets you closer to the secure network that you want.
Here to Help
Realize that your business may have specific security or compliance needs that we haven’t addressed here. Each organization is different, and your security solution should be tailored to meet those needs.
If you find this whole thing overwhelming, or don’t think that you have the time you need to get your company where it needs to be, i.t.NOW is here to help. Our team of experts is standing by ready to take the burden of IT security off your shoulders. A partnership with i.t.NOW allows you to focus on growing your business and day to day operations, while the experts worry about your network security.
Call us today for a FREE network security evaluation. We’ll give you a report card that’s easy to read and expert recommendations on how to secure your network. No nonsense or technobabble, just smart solutions from a team of experts.


